Smart strategy saves thousands mortgage rate lock vs float
When you're navigating the complex world of mortgages, understanding whether to lock in your rate or let it float can save you thousands, and by taking the time to browse options and visit websites, you can make the most informed decision.
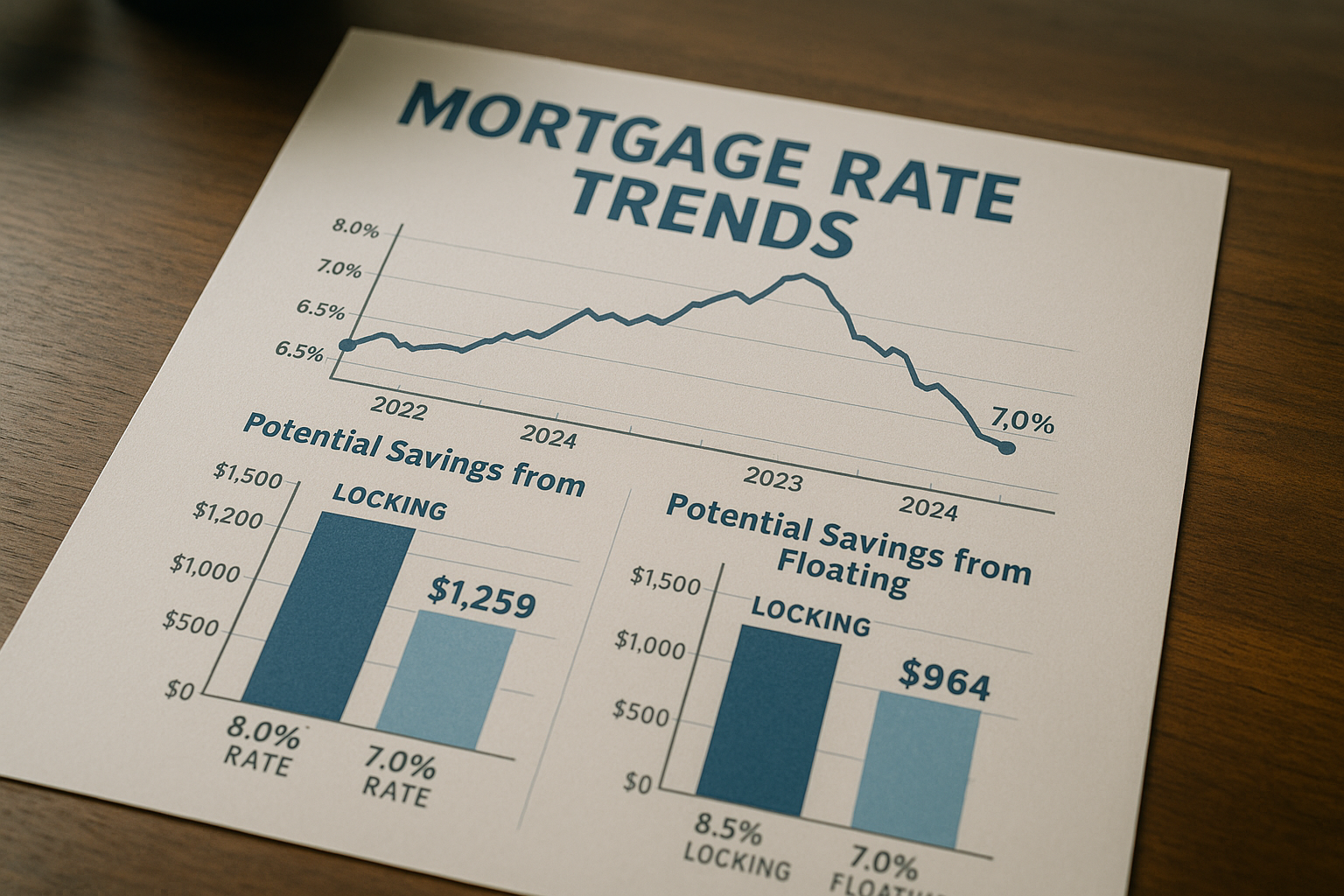
Understanding Mortgage Rate Lock vs. Float
Securing a mortgage is one of the most significant financial commitments you'll make, and the decision to lock or float your interest rate can dramatically impact your financial future. A mortgage rate lock is an agreement between you and your lender to secure a specific interest rate for a set period, typically ranging from 30 to 60 days. This can protect you from potential rate increases while your loan is processed. Conversely, choosing to float your rate means you’re opting to let the interest rate fluctuate until the loan is finalized, which could potentially result in a lower rate if market conditions improve.
Benefits of Locking Your Rate
Locking in your mortgage rate offers stability and peace of mind. In a volatile interest rate environment, a rate lock ensures that you are protected from any sudden increases that could make your mortgage more expensive. For instance, if you lock in a rate at 3.5% and rates climb to 4% before closing, you’ll still benefit from the lower rate. This predictability allows you to plan your budget more effectively, knowing exactly what your monthly payments will be.
The Case for Floating Your Rate
On the other hand, floating your rate can be advantageous if you anticipate that interest rates will decrease. By not locking in immediately, you may benefit from a lower rate, reducing your overall mortgage costs. This strategy requires careful monitoring of market trends and economic indicators, as rates can be influenced by various factors, including Federal Reserve policies and inflation rates. For example, if rates are expected to drop due to an economic downturn, floating might be a wise choice.
Real-World Examples and Statistics
Consider the scenario of a $300,000 mortgage. Locking in a rate at 3.5% versus floating to potentially secure a 3.25% rate could save you approximately $15,000 over a 30-year term1. However, if rates rise to 3.75% instead, locking early could save you nearly $20,000 in interest costs. According to Freddie Mac, the average 30-year fixed mortgage rate has seen fluctuations of up to 0.5% within a few months, underscoring the importance of timing2.
Strategies to Decide
Deciding whether to lock or float involves evaluating your risk tolerance and understanding market conditions. Consulting with a financial advisor or mortgage broker can provide personalized insights based on your specific situation. Additionally, many lenders offer a "float-down" option, allowing you to lock in a lower rate if rates drop after you've locked, typically for a fee. This can be a valuable middle-ground strategy for those hesitant to commit to a full lock or float decision.
Exploring Your Options
As you weigh your options, keep in mind that different lenders offer various rate lock periods and floating policies. It's crucial to compare these carefully. By visiting websites of reputable lenders and exploring their rate lock policies, you can find terms that align with your financial goals. Remember, the right choice can lead to significant savings over the life of your mortgage.
Ultimately, whether you choose to lock or float your mortgage rate, being informed and proactive can help you navigate this financial decision with confidence. By following the options and exploring specialized resources, you can ensure that you make the best choice for your financial future.