Unraveling the Paleo vs Keto Diet Debate: Which Delivers Optimal Health and Nutrition?
Over the past decade, the Paleo and Keto diets have gained considerable popularity for their potential health and weight loss benefits. Both diets emphasize whole, unprocessed foods and restrict the consumption of carbohydrates. While they share similarities, there are distinct differences in their macronutrient composition and recommended food sources. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the Paleo vs Keto diet debate and examine their effects on health, nutrition, and weight loss.
Understanding the Paleo Diet

The Paleo diet, also known as the Paleolithic or Caveman diet, is based on the presumed dietary patterns of early humans during the Paleolithic era. It focuses on consuming foods that were available to our ancestors, such as lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. This diet excludes grains, legumes, dairy products, processed foods, and refined sugars.
The main principle behind the Paleo diet is that our bodies are genetically adapted to thrive on the same foods our ancestors consumed. Proponents argue that the modern diet, filled with processed foods and sugar-laden beverages, is to blame for many of today's chronic diseases, including obesity and heart disease.
Benefits of the Paleo Diet
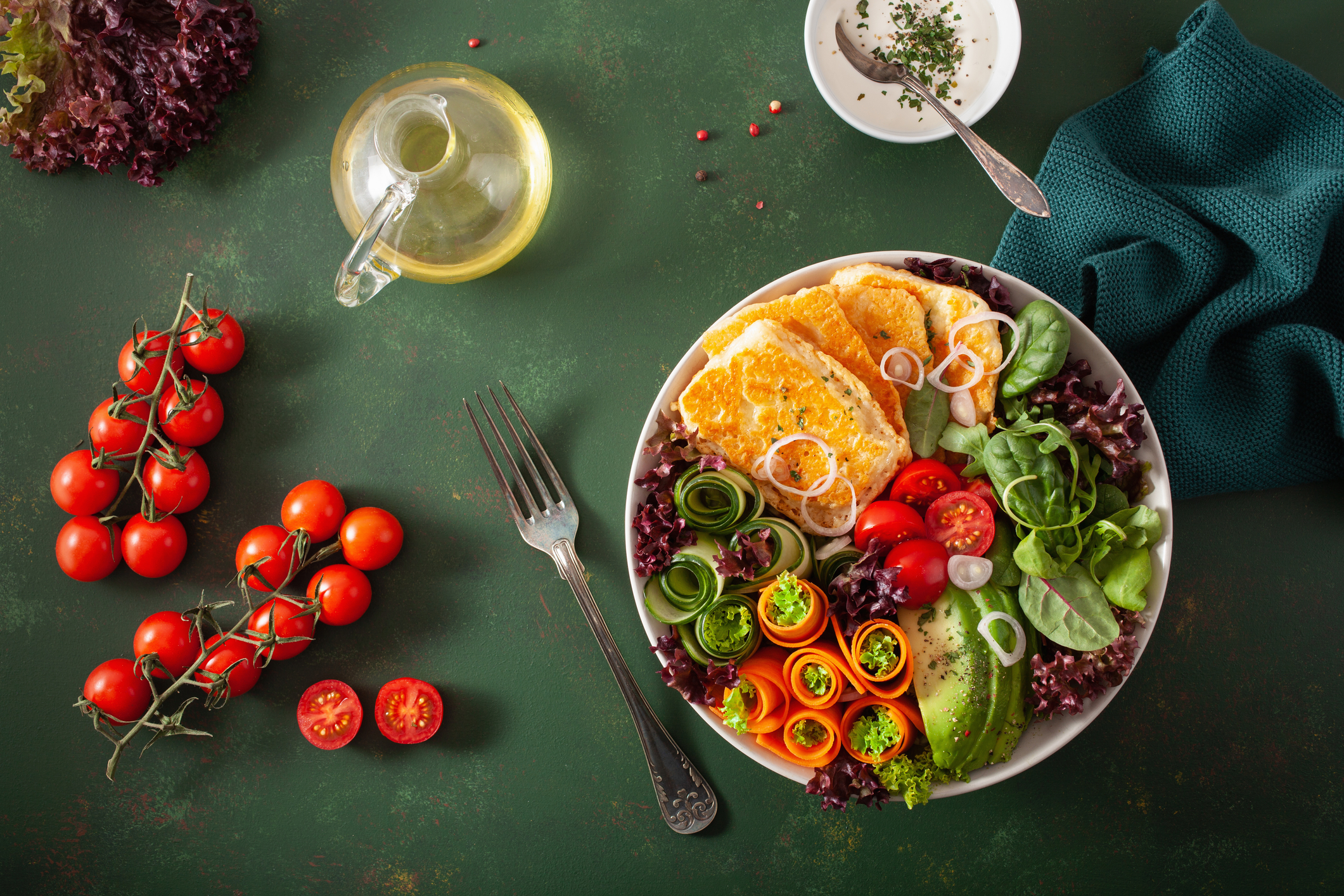
One of the main advantages of the Paleo diet is its emphasis on whole, nutrient-dense foods. By eliminating processed foods and added sugars, followers of the Paleo diet often experience weight loss, improved blood glucose control, and increased energy levels.
The high protein content of the diet, which comes from lean meats and fish, promotes satiety and helps preserve muscle mass. The inclusion of fruits and vegetables provides a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, supporting overall health and immune function.
However, critics of the Paleo diet argue that its restrictive nature may lead to nutrient deficiencies, particularly in calcium, vitamin D, and fiber. Its exclusion of grains and legumes, which are nutrient-dense and provide important dietary fiber, is often a point of contention.
Exploring the Keto Diet

The Keto diet, short for ketogenic, is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that has gained popularity for its rapid weight loss results. The primary goal of this diet is to induce a state of ketosis, where the body relies on ketones, produced from stored fat, as its main source of energy.
The Keto diet typically consists of 70-75% calories from fat, 20-25% from protein, and only 5-10% from carbohydrates. This extreme reduction in carbohydrates forces the body to switch from carbohydrate metabolism to fat metabolism.
Benefits of the Keto Diet

The Keto diet has been praised for its ability to lead to rapid weight loss, primarily through fat loss. When carbohydrate intake is limited, the body depletes its glycogen stores and starts breaking down stored fat for energy. This process can result in significant reductions in body weight and body fat percentage.
Additionally, the Keto diet has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and blood glucose control. This is especially beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or those struggling with insulin resistance.
Critics of the Keto diet highlight its potential drawbacks, such as nutrient deficiencies, increased risk of heart disease due to a high intake of saturated fats, and the challenge of sustaining the diet long-term.
Finding Common Ground

While the Paleo and Keto diets have distinct differences, they also share some common ground. Both diets prioritize whole, unprocessed foods and discourage the consumption of processed sugars, refined grains, and vegetable oils.
They also both promote weight loss by limiting carbohydrates and incorporating a higher proportion of protein and fat in the diet. However, their macronutrient ratios differ, with the Keto diet being much higher in fat and lower in protein compared to the Paleo diet.
When it comes to sustainability, the Paleo diet may offer more flexibility. It allows for the inclusion of certain carbohydrates, like sweet potatoes and some fruits, which can better fit into a long-term eating plan. On the other hand, the strict carbohydrate restrictions of the Keto diet may be challenging for many individuals to maintain over an extended period.
Tailoring the Diet to Individual Needs

Ultimately, the choice between the Paleo and Keto diets depends on individual preferences, health goals, and metabolic considerations. It is essential to work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the most suitable approach for your specific needs.
For those looking to improve overall health and eat in a way that closely aligns with our evolutionary heritage, the Paleo diet may be a good fit. It emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods and encourages the elimination of highly processed options.
On the other hand, if rapid weight loss and improved blood glucose control are primary objectives, the Keto diet may be worth considering. However, it is crucial to monitor blood lipid levels and consult with a healthcare professional to mitigate any potential risks associated with the high-fat nature of the diet.
The Paleo vs Keto diet debate offers varied perspectives on achieving optimal health and nutrition. Both diets emphasize a shift away from highly processed foods towards whole, unprocessed options. The choice between the two ultimately depends on an individual's specific goals and preferences.
Regardless of which diet is followed, it is essential to prioritize nutrient-dense foods, ensure proper hydration, and maintain a balanced approach to sustainable long-term results. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance and support throughout the journey towards optimal health and nutrition.